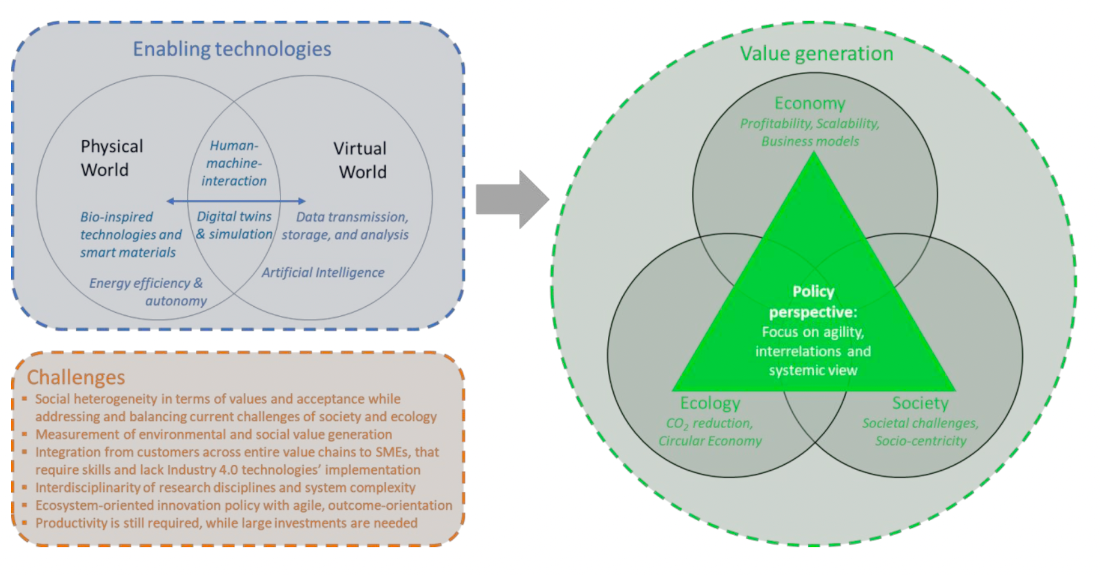
Enabling Technologies for Industry 5.0
Industry 5.0 recognises the power of industry to achieve societal goals beyond jobs and growth to become a provider of prosperity, by making production respect the boundaries of our planet and placing the wellbeing of the industry worker at the centre of the production process
1) Individualised Human-machine-interaction
To link humans with technologies, support humans and combine human innovation and machines capabilities. The following technologies support humans in physical and cognitive tasks:
- Multi-lingual speech and gesture recognition and human intention prediction Tracking technologies for mental and physical strain and stress of employees
- Robotics: Collaborative robots (‘cobots’), which work together with humans and assist humans
- Augmented, virtual or mixed reality technologies, especially for training and inclusiveness
- Enhancing physical human capabilities: Exoskeletons, bio-inspired working gear and safety equipment
- Enhancing cognitive human capabilities: Technologies for matching the strengths of Artificial Intelligence and the human brain (e.g., combining creativity with analytical skills), decision support systems
2) Bio-inspired technologies and smart materials
Bio-inspired technologies and processes stemming from the concept of Biological Transformation can be integrated with, for instance, the following properties:
- Self-healing or self-repairing
- Lightweight
- Recyclable
- Raw material generation from waste
- Integration of living materials
- Embedded sensor technologies and biosensors Adaptive/responsive ergonomics and surface properties Materials with intrinsic traceability
3) Digital twins and simulation
Digital twins and simulation technologies optimise production, test products and processes and detect possible harmful effects, for instance:
- Digital twins of products and processes
- Virtual simulation and testing of products and processes (e.g., for human-centricity, working and operational safety)
- Multi-scale dynamic modelling and simulation
- Simulation and measurement of environmental and social impact
- Cyber-physical systems and digital twins of entire systems
- Planned maintenance
4) Data transmission, storage, and analysis technologies
Energy-efficient and secure data transmission, storage, and analysis technologies are required, with properties such as:
- Networked sensors
- Data and system interoperability
- Scalable, multi-level cyber security
- Cyber security/safe cloud IT-infrastructure
- Big data management
- Traceability (e.g., data origin and fulfilment of specifications)
- Data processing for learning processes
- Edge computing
5) Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence, nowadays often still referring to advanced correlation analysis technologies, must be developed further in several regards:
- Causality-based and not only correlation-based artificial intelligence
- Show relations and network effects outside of correlations
- Ability to respond to new or unexpected conditions without human support
- Swarm intelligence
- Brain-machine interfaces
- Individual, person-centric Artificial Intelligence
- Informed deep learning (expert knowledge combined with Artificial Intelligence)
- Skill matching of humans and tasks
- Secure and energy-efficient Artificial Intelligence
- Ability to handle and find correlations among complex, interrelated data of different origin and scales in dynamic systems within a system of systems
6) Technologies for energy efficiency, renewables, storage and autonomy
As the majority of technologies mentioned requires large amounts of energy to operate, the following technologies and properties are required to achieve emission neutrality:
- Integration of renewable energy sources
- Support of Hydrogen and Power-to-X technologies
- Smart dust and energy-autonomous sensors
- Low energy data transmission and data analysis
For more infomation visit the official website of the European Union: Enabling Technologies for Industry 5.0



